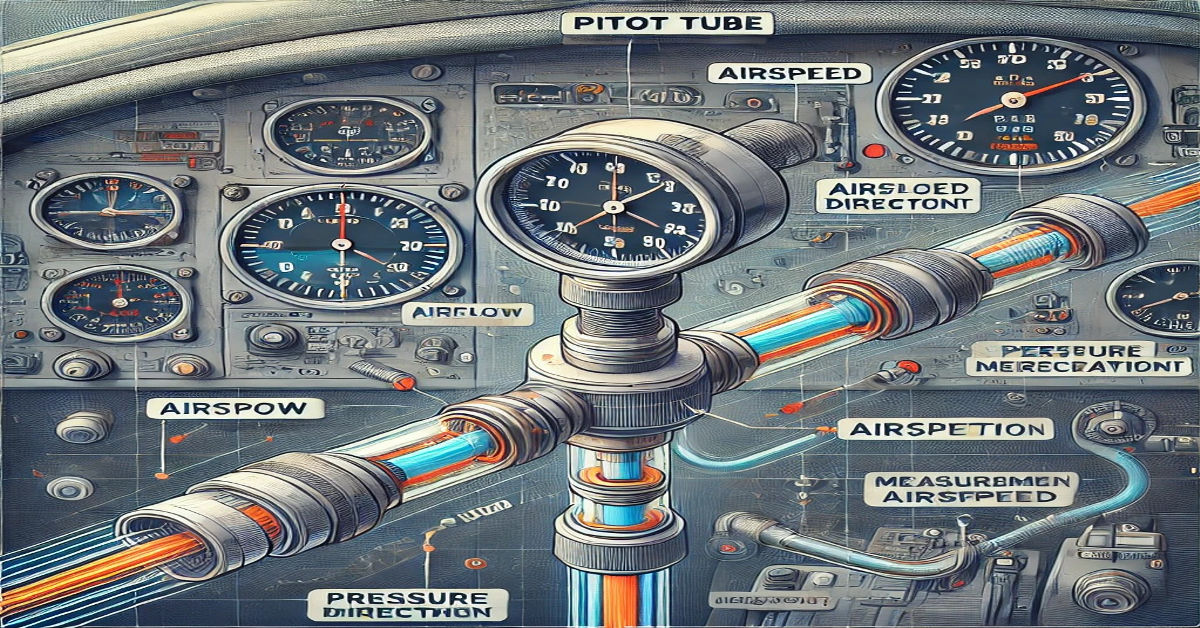
Have you ever wondered how airplanes measure their speed or how engineers determine the velocity of fluids in pipelines? The answer lies in a simple yet highly effective device known as the pitot tube. Named after Henri Pitot who invented it in the early 18th century this instrument plays a crucial role in various industries from aviation to fluid mechanics. Despite its simple design, the pitot tube provides accurate measurements of fluid flow velocity making it indispensable for engineers, pilots and scientists alike. This article explores how a pitot tube works, its applications, and why it continues to be a vital tool in modern technology.
What is a Pitot tube?
A pitot tube is a flow measurement device used to determine the velocity of a fluid—be it air or liquid. It consists of a hollow tube that faces directly into the fluid flow, allowing it to capture both the static and dynamic pressures. By measuring the difference between these pressures, the pitot tube calculates the fluid’s velocity. Its simplicity, accuracy, and reliability make it a preferred choice in various fields, particularly in aviation and fluid dynamics studies.
How Does a Pitot tube Work?
The pitot tube operates on the principle of Bernoulli’s equation, which relates the pressure, velocity, and height of a moving fluid. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how it works:
- Dynamic Pressure Measurement: The open end of the pitot tube faces the fluid flow, allowing it to measure the dynamic pressure caused by the fluid’s movement.
- Static Pressure Measurement: Small holes on the side of the tube measure the static pressure, which is the pressure exerted by the fluid at rest.
- Velocity Calculation: By subtracting the static pressure from the total pressure (measured at the open end), the device calculates the dynamic pressure. The fluid’s velocity is then derived using the relationship established by Bernoulli’s equation.
Components of a Pitot tube
A standard pitot tube includes the following parts:
- Main Tube: Faces the flow to measure total pressure.
- Static Ports: Small holes along the sides to capture static pressure.
- Support Structure: Holds the pitot tube in place and connects it to pressure sensors.
- Pressure Transducer: Converts the pressure readings into measurable velocity data.
Types of Pitot tubes
Different types of pitot tubes cater to various applications and measurement needs:
Standard Pitot tube
The basic design includes a single tube that measures total pressure and static pressure through separate ports.
Pitot-Static tube
This type integrates both the pitot tube and static ports into a single device, commonly used in aircraft to measure airspeed.
Multi-Hole Pitot tube
Equipped with multiple ports, this variant provides more accurate readings in turbulent or multi-directional flow conditions.
S-Type Pitot tube
Used in industrial applications, the S-type features an S-shaped design to measure gas flow in ducts and stacks.
Applications of Pitot tubes
The versatility of the pitot tube allows it to be used in a wide range of industries and scenarios:
Aviation
One of the most well-known uses of the pitot tube is in aviation, where it measures an aircraft’s airspeed. Mounted on the exterior of the aircraft, it provides pilots with crucial data for safe and efficient flight operations.
Wind Tunnel Testing
Engineers use pitot tubes in wind tunnels to measure airflow over vehicle models, helping improve aerodynamics in cars, planes, and even buildings.
HVAC Systems
In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, pitot tubes measure airflow in ducts, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency.
Industrial Fluid Flow Measurement
Pitot tubes monitor liquid flow in pipelines within industries like oil and gas, water treatment, and chemical processing.
Marine Navigation
Ships use pitot tubes to measure water speed relative to the vessel, aiding navigation and fuel efficiency.
Advantages of Using a Pitot tube
Pitot tubes offer several benefits that make them a popular choice in fluid velocity measurement:
- Simple Design: Easy to install and maintain, requiring minimal equipment.
- Cost-Effective: Provides accurate measurements at a lower cost compared to other flow measurement devices.
- Versatile: Suitable for both liquid and gas flow measurements across various industries.
- Minimal Flow Disruption: Its streamlined design causes little interference with the fluid flow.
- High Accuracy in Steady Flows: Particularly effective in stable, laminar flow conditions.
Limitations of a Pitot tube
While pitot tubes are highly useful, they do have some limitations:
- Sensitivity to Flow Direction: Accuracy decreases if the tube is not properly aligned with the fluid flow.
- Not Ideal for Low-Speed Flows: Measuring very low velocities can lead to inaccuracies.
- Susceptible to Blockages: Debris or ice can obstruct the tube, especially in aviation applications.
- Limited Use in Turbulent Flows: Performance may be compromised in highly turbulent or multi-directional flows unless a multi-hole variant is used.
How to Use a Pitot tube Effectively
To ensure accurate readings, proper usage and maintenance of a pitot tube are essential:
- Correct Alignment: Always align the tube directly with the fluid flow for accurate pressure measurements.
- Regular Maintenance: Clean the tube to prevent blockages from debris or environmental factors.
- Use with Pressure Transducers: Connect the tube to reliable sensors for precise data collection.
- Monitor for Ice Formation: In aviation, pitot heaters prevent icing that can block the tube.
Pitot tube in Aviation: A Closer Look
In aircraft, pitot tubes play a vital role in providing airspeed information. Pilots rely on this data for crucial decisions during takeoff, cruising, and landing. Any malfunction in the pitot system, such as blockages, can lead to incorrect readings and potentially hazardous situations. That’s why regular inspections and the use of pitot tube heaters are standard practices in aviation.
Safety Considerations in Using Pitot tubes
While using a pitot tube, especially in critical applications like aviation, certain safety measures should be taken:
- Inspect Before Use: Ensure the tube is clean and unobstructed.
- Use Protective Covers: When not in use, cover the pitot tube to prevent foreign object entry.
- Monitor Environmental Conditions: Be aware of weather conditions that could cause icing or debris accumulation.
- Regular Calibration: Periodically calibrate the pitot system to maintain accuracy.
Innovations and Technological Advancements
Modern technology has improved the traditional pitot tub’e design. Advances include:
- Digital Integration: Combining pitot tubes with electronic sensors for real-time data analysis.
- Smart Sensors: Enhanced pitot tubes now feature sensors that detect blockages and environmental changes.
- Miniaturization: Compact designs are being developed for drones and small unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using a Pitot tube
- Incorrect Installation: Misalignment with the flow direction can lead to inaccurate readings.
- Ignoring Maintenance: Neglecting to clean and inspect the tube can cause blockages.
- Overlooking Calibration: Failure to calibrate can compromise measurement accuracy.
- Using in Unsuitable Conditions: Avoid using standard pitot tubes in turbulent or multi-directional flows without appropriate variants.
Future of Pitot tube Technology
As industries demand more precise and reliable data, the pitot tub’e continues to evolve. Developments focus on enhancing durability, accuracy, and adaptability to challenging environments. Integration with IoT (Internet of Things) and wireless data transmission could revolutionize how pitot tub’es are used in remote and automated applications.
How to Select the Right Pitot tube for Your Needs
Choosing the appropriate pitot tub’e depends on several factors:
- Flow Conditions: Determine if the application involves steady, turbulent, or multi-directional flow.
- Fluid Type: Consider whether you’re measuring air, water, or other liquids.
- Environmental Factors: Account for temperature, pressure, and potential debris in the flow.
- Accuracy Requirements: Higher accuracy needs may require multi-hole or advanced pitot tubes.
Conclusion
The pitot tube remains a fundamental tool in measuring fluid velocity, offering simplicity, reliability, and versatility across various industries. Whether you’re flying an aircraft, managing an HVAC system, or studying fluid dynamics, understanding how a pitot tub’e works and how to use it effectively can make a significant difference in obtaining accurate data. As technology continues to advance, pitot tubes are being refined to meet modern demands while retaining the core principles that have made them indispensable for centuries.
FAQs
Q1: What is the primary use of a pitot tub’e?
It measures the velocity of flowing fluids, commonly used in aviation and fluid dynamics.
Q2: How does a pitot tub’e measure airspeed?
It calculates airspeed by comparing the dynamic and static pressures of the airflow.
Q3: Can a pitot tub’e be used for liquids?
Yes, it measures the velocity of both gases and liquids in various applications.
Q4: What causes a pitot tub’e to malfunction?
Blockages from debris, ice formation, or improper installation can affect its accuracy.
Q5: How often should a pitot tub’e be maintained?
Regular inspections and cleaning should be performed, especially in critical applications like aviation.
Q6: Is a pitot tub’e suitable for measuring turbulent flows?
Standard pitot tubes may struggle with turbulent flows, but multi-hole variants offer better accuracy.